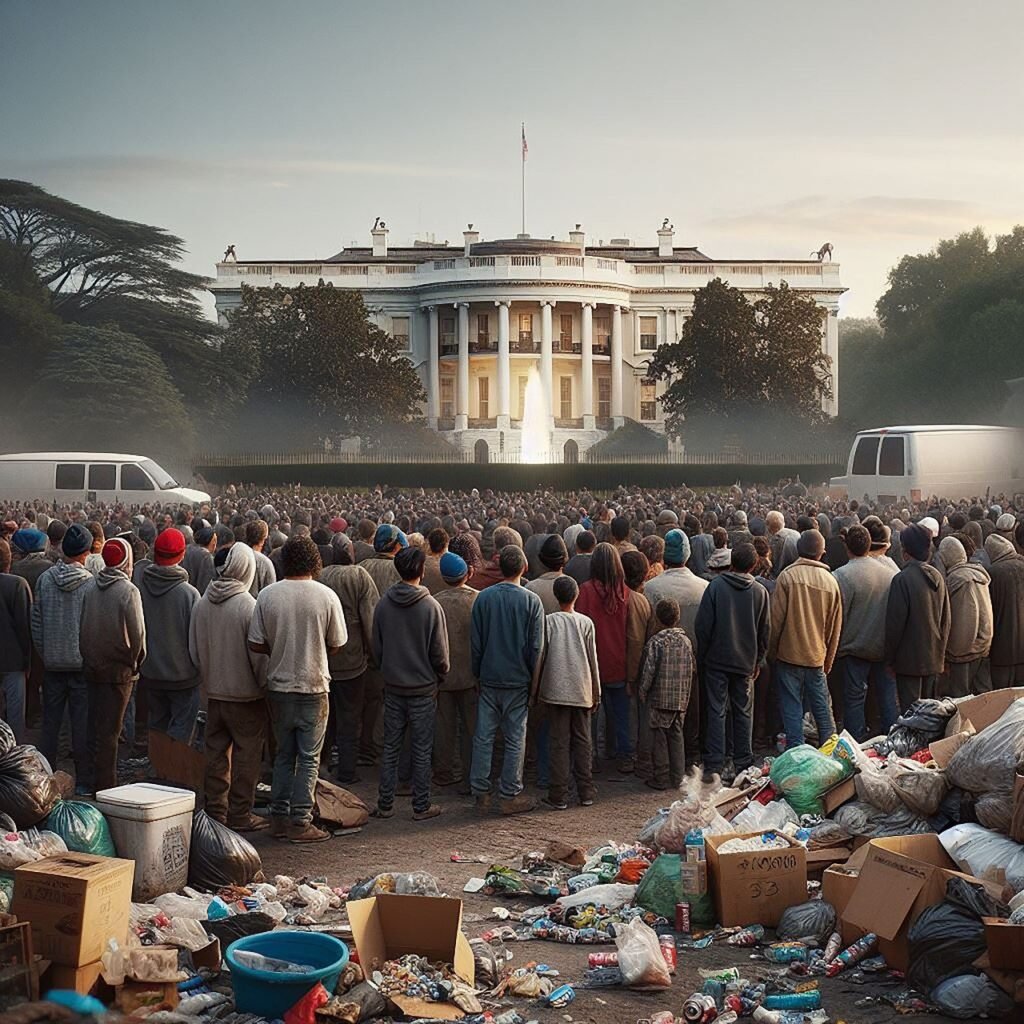
Unemployment in Pakistan is a critical issue with extensive ramifications for the nation’s economic, social, and political stability. This comprehensive analysis delves into the underlying causes, effects, and potential solutions to this pressing problem.
Causes of Unemployment in Pakistan
Lack of Education and Skill Development
Weaknesses in Pakistan’s Education System
Pakistan’s education system struggles with outdated curricula, inadequate infrastructure, and a shortage of qualified teachers. These deficiencies result in a skills gap that hinders students’ ability to compete effectively in the job market.
Gaps in Technical and Vocational Training
Many young individuals lack access to quality technical and vocational training programs. This shortage of practical skills relevant to the job market limits their employability and contributes to high unemployment rates.
Economic Factors
Slow Growth in Industrial Sector
The industrial sector in Pakistan has not expanded rapidly enough to accommodate the growing workforce. Challenges such as energy shortages, political instability, and insufficient investment have stunted industrial growth, impacting job creation.
Challenges in the Agricultural Sector
Despite agriculture being a cornerstone of Pakistan’s economy, inefficiencies, outdated technology, and poor infrastructure hamper its ability to generate sustainable employment opportunities.
Rapid Population Growth
High Population Growth Rate
With one of the highest population growth rates globally, Pakistan faces immense pressure on its job market. The growing population exacerbates the unemployment crisis by outpacing the creation of new job opportunities.
Political and Social Instability
Political Uncertainty and Economic Impact
Frequent changes in government policies and political instability undermine investment and economic growth, crucial for job creation.
Security Issues Affecting Investment
Ongoing security concerns deter both domestic and foreign investments, further limiting job opportunities and economic development.
Economic Inequality and Regional Disparities
Urban-Rural Divide
Significant disparities exist between urban and rural areas regarding economic development and employment opportunities. Rural areas, in particular, face high unemployment rates due to limited resources and opportunities.
Effects of Unemployment in Pakistan
Economic Effects
Reduced Economic Growth
High unemployment leads to lower consumer spending, which stagnates economic growth. Unemployed individuals have less money to spend, impacting businesses and overall economic health.
Increasing Poverty Levels
Unemployment directly contributes to rising poverty rates, as individuals and families struggle to meet basic needs without a steady income.
Social Effects
Mental Health Challenges
Extended periods of unemployment can lead to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Financial insecurity and a lack of purpose significantly affect individuals’ well-being.
Social Unrest
High unemployment rates, particularly among the youth, can lead to social unrest. This unrest may manifest as increased crime rates, protests, and political instability.
Political Implications
Erosion of Public Trust
Persistent unemployment can erode public trust in government institutions, leading to political instability and governance challenges.
National Security Concerns
Economic instability and high unemployment rates can contribute to recruitment by extremist and criminal groups, posing threats to national security.
Constraints in Controlling Unemployment
Lack of Job Opportunities
Insufficient Job Creation
The rate of job creation has not kept up with the growing labor force. Economic policies and measures to create employment have been insufficient.
Health Limitations
Access to Health Care
Poor health and limited access to healthcare services can inhibit individuals’ ability to work and find employment.
Financial Constraints
Limited Access to Credit
Many individuals, especially in rural areas, lack access to credit and financial resources to start businesses or pursue further education and training.
Psychological Barriers
Erosion of Confidence
Long-term unemployment can diminish self-esteem and motivation, making it challenging for individuals to secure employment.
Age and Discrimination Issues
Age Discrimination
Older individuals and disadvantaged groups often face discrimination in the job market, reducing their employment opportunities.
Technological Constraints
Digital Divide
Limited access to technology and the Internet, particularly in rural areas, hinders job seekers’ ability to find employment and develop necessary skills.
Potential Solutions to Address Unemployment
Educational Reforms
Modernizing the Curriculum
Updating educational curricula to align with market demands and improving educational quality at all levels can enhance employability.
Expanding Technical and Vocational Education
Investing in technical and vocational training programs can equip individuals with practical skills needed in various industries.
Economic Policies
Promoting Industrial Development
Implementing policies that support industrial growth, such as providing investor incentives and improving infrastructure, can create job opportunities.
Supporting Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Facilitating access to credit and resources for SMEs can boost entrepreneurship and generate employment.
Agricultural Development
Modernizing Agricultural Practices
Adopting modern technology, improving irrigation systems, and providing training to farmers can enhance productivity and create job opportunities in agriculture.
Population Control Measures
Family Planning Programs
Promoting family planning and awareness programs can help control population growth and reduce pressure on the job market.
Political Stability and Security
Ensuring Political Stability
Consistent government policies and political stability can encourage investment and economic growth.
Enhancing Security Measures
Improving security can create a more conducive environment for investment and economic development.
Addressing Regional Disparities
Investing in Rural Development
Investing in rural infrastructure, education, and healthcare can help bridge the urban-rural divide and create job opportunities in rural areas.
Strengthening Social Safety Nets
Implementing Unemployment Benefits
Providing unemployment benefits and social safety nets can offer temporary relief to unemployed individuals and their families.
Leveraging Technology
Promoting Digital Literacy
Enhancing digital literacy and access to technology can help job seekers find employment opportunities and develop relevant skills.
Conclusion
Unemployment in Pakistan is a multifaceted challenge that requires a holistic and integrated approach. By implementing educational reforms, promoting industrial and agricultural development, ensuring political stability, and addressing regional disparities, Pakistan can foster a more inclusive and robust labor market. Collaborative efforts from the government, private sector, and civil society are essential to provide sustainable employment opportunities and improve the quality of life for all citizens.
Addressing unemployment is crucial not only for economic growth but also for social cohesion and national security. With targeted policies and initiatives, Pakistan can overcome the challenges of unemployment and pave the way for a prosperous future.